Understanding Expensive Assets and Their Financial Impact
Expensive assets, such as real estate, industrial machinery, luxury vehicles, or advanced medical equipment, require significant capital investments. These purchases often exceed the liquidity reserves of individuals and businesses, making financing essential. According to a 2023 Federal Reserve report, 67% of businesses rely on external funding to acquire high-value assets, highlighting the importance of strategic financial planning.
The financial impact of acquiring such assets extends beyond the initial purchase. Maintenance, insurance, and depreciation costs can strain budgets if not accounted for. For example, commercial real estate loses 2-5% of its value annually due to depreciation, while machinery may require repairs costing up to 20% of its original price. Platforms like BorrowBe offer solutions to offset these costs by enabling users to Turn Your Assets Into Income, converting underutilized resources into revenue streams.
Common Examples of Expensive Assets
- Real Estate: Residential properties, commercial buildings, vacation rentals.
- Vehicles: Luxury cars, construction trucks, aviation equipment.
- Industrial Machinery: Manufacturing robots, agricultural tractors.
- Technology: Data servers, medical imaging systems.
Types of Financing Options for Expensive Assets
Selecting the right financing method depends on factors like cash flow, creditworthiness, and asset lifecycle. Below are the most common options:
Traditional Bank Loans
Bank loans provide upfront capital with fixed or variable interest rates. They’re ideal for borrowers with strong credit scores (680+), offering terms ranging from 5 to 30 years. However, approval processes are stringent, with banks requiring collateral and detailed financial histories.
Pros:
- Lower interest rates (4-8% APR).
- Predictable repayment schedules.
Cons:
- Lengthy approval timelines (2-6 weeks).
- High collateral requirements.
Leasing
Leasing allows businesses to use assets without ownership, reducing upfront costs. A 2022 Equipment Leasing and Finance Association study found that 80% of U.S. companies lease equipment. This model is particularly effective for technology or machinery with rapid obsolescence cycles.
Types of Leases:
- Operating Lease: Short-term, cancelable agreements (e.g., Car for Lease).
- Capital Lease: Long-term, ownership-transferable contracts.
Asset-Based Lending
Asset-based loans use the financed asset as collateral, making them accessible to borrowers with lower credit scores. For instance, a $500,000 loan for construction machinery might require the equipment itself as security. Interest rates are typically higher (8-15%), but approval is faster.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending
P2P platforms connect borrowers directly with investors, bypassing traditional institutions. Rates vary widely (5-20%), depending on risk assessments. This option suits those seeking flexible terms, though default risks are higher.
|
Financing Type |
Interest Rate |
Term Length |
Best For |
|
Bank Loan |
4-8% |
5-30 years |
Stable businesses |
|
Leasing |
6-12% |
1-5 years |
Tech or machinery |
|
Asset-Based Lending |
8-15% |
1-10 years |
Collateral-rich borrowers |
|
P2P Lending |
5-20% |
1-7 years |
Flexible terms |

Factors to Consider When Choosing a Financing Option
Credit Score and Financial History
Lenders prioritize credit scores to assess risk. For example, traditional banks require a minimum score of 680, while P2P platforms may accept scores as low as 600. Regularly review your credit report and resolve discrepancies before applying.
Interest Rates and Fees
Compare APRs, origination fees, and prepayment penalties. A 1% difference in interest can save $10,000 over a $200,000 loan. Use online calculators or consult platforms like BorrowBe to Post an Ad for competitive offers.
Asset Depreciation and Resale Value
Assets like vehicles lose 20-30% of their value in the first year. Opt for shorter-term financing if depreciation is steep. Alternatively, lease agreements transfer residual value risks to the lessor.
Cash Flow and Budget Flexibility
Ensure monthly payments align with revenue cycles. For seasonal businesses, lines of credit or Vacation Rental income through BorrowBe can supplement cash reserves during low-demand periods.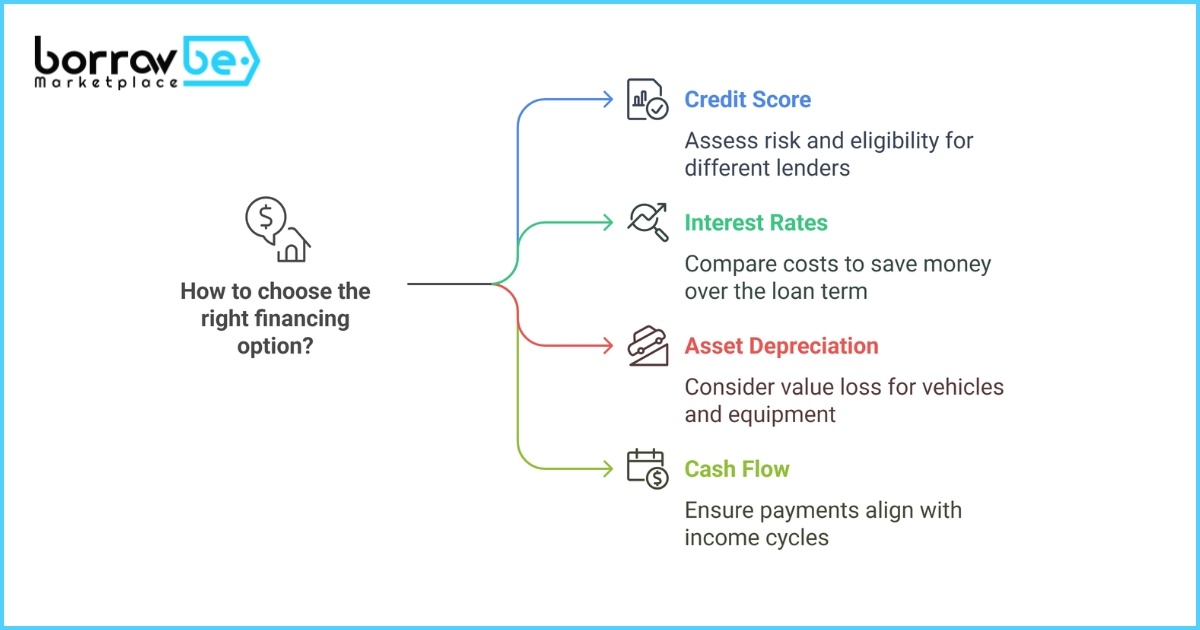
Case Studies and Real-World Scenarios
Small Business Machinery Acquisition
A construction firm needed a $250,000 excavator but lacked upfront capital. By opting for an asset-based loan at 10% APR, they secured financing within a week using the equipment as collateral. Monthly payments were structured to align with project cash flows.
Luxury Car Financing
An individual leased a luxury vehicle through BorrowBe’s Car for Lease platform, paying $1,200 monthly instead of a $100,000 upfront cost. After three years, they upgraded to a newer model without resale hassles.
Real Estate Investment
An investor purchased a $1.2M commercial property using a 25-year bank loan at 5.5% APR. By listing part of the space as a House for Rent, they generated $8,000 monthly, covering 70% of the mortgage.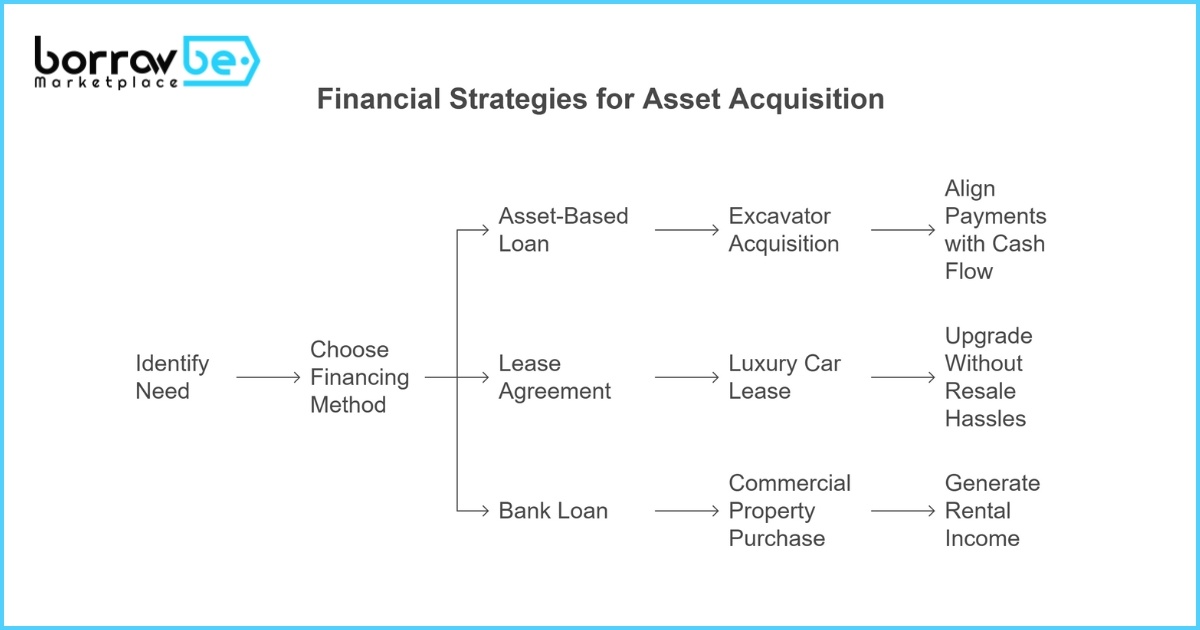
How does leasing differ from taking a loan?
Leasing allows temporary asset use without ownership, often with lower monthly payments and maintenance included. Loans involve full ownership after repayment but require higher upfront equity. Leasing suits rapidly depreciating assets, whereas loans are better for long-term investments.
Can I finance an asset with bad credit?
Yes, asset-based lending or P2P platforms may accept lower credit scores if collateral is provided. Alternatively, improving your credit by paying down debts or using co-signers can expand options.
What are the tax benefits of financing expensive assets?
Interest payments on loans and lease expenses are often tax-deductible for businesses. Consult a tax advisor to maximize deductions based on your jurisdiction.
How can I reduce risks when financing?
Diversify income streams by monetizing underused assets. For example, rent out idle equipment via BorrowBe’s Construction Machinery portal or use their app (Download Here) to manage payments efficiently.





